What is Tooth Whitening?
Tooth whitening, also known as teeth bleaching, is a cosmetic dental procedure designed to lighten the shade of your teeth. It’s a popular choice for people looking to enhance their smiles by removing stains and discoloration caused by factors like coffee, tea, tobacco, and aging. The process typically involves using bleaching agents, such as hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, which penetrate the enamel and dentin to break down staining compounds. Professional tooth whitening can achieve significant results, often several shades lighter, while at-home kits offer a more gradual and controlled approach. The effectiveness of tooth whitening depends on the type of stains, the concentration of the bleaching agent, and the duration of the treatment. Many people opt for tooth whitening to boost their confidence and achieve a brighter, more youthful smile.
Types of Tooth Whitening Procedures
There are several methods for teeth whitening, each with its own set of advantages and considerations. Professional in-office whitening is performed by a dentist and offers the most dramatic results in a short amount of time. This typically involves applying a high-concentration bleaching agent to the teeth, often activated by a special light or laser. At-home whitening kits, prescribed or over-the-counter, provide a more gradual approach. These kits usually include custom-fitted or pre-formed trays and a lower concentration bleaching gel. Whitening toothpastes and mouthwashes are another option, designed to remove surface stains, but they are less effective for deep-seated discoloration. The best choice depends on individual needs, the severity of the staining, and personal preferences. It’s important to consult with a dentist to determine the most appropriate method and ensure it’s safe and effective for your specific situation.
In-Office Whitening

In-office tooth whitening, conducted by a dental professional, offers the most immediate and significant results. The procedure typically involves isolating the gums and lips to protect them from the bleaching agent, which is a high-concentration hydrogen peroxide solution. The dentist applies the whitening agent to the teeth and may use a special light or laser to accelerate the process. This can enhance the bleaching effect. The entire treatment usually takes about an hour and can lighten teeth several shades in a single session. Professional in-office whitening is ideal for people seeking fast and dramatic improvements. However, it can be more expensive than at-home methods. It’s essential to consult with a dentist to determine if in-office whitening is suitable for your dental health and needs. They will assess your teeth and gums to ensure the procedure is safe and effective for you. The dentist also provides guidance on maintaining the results.
At-Home Whitening Kits
At-home tooth whitening kits provide a convenient and cost-effective alternative to professional treatments. These kits come in various forms, including custom-fitted trays, pre-formed trays, strips, and whitening toothpastes. Custom-fitted trays, obtained from a dentist, offer the best fit and ensure even distribution of the whitening agent. Over-the-counter kits are readily available. They use pre-formed trays or strips. The bleaching agents in these kits typically contain lower concentrations of hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide compared to in-office treatments. The process usually involves applying the whitening gel to the trays or strips and wearing them for a specified time, typically 30 minutes to an hour daily, for a few weeks. At-home whitening kits are suitable for people who prefer a more gradual approach. They offer flexibility and can be done in the comfort of your home. However, results may take longer to appear. It’s essential to follow the instructions carefully to ensure safe and effective usage.
Is Tooth Whitening Safe During Breastfeeding?
The safety of tooth whitening during breastfeeding is a common concern, and it’s crucial to approach this topic with caution. There is limited research on the effects of tooth whitening agents on breast milk and, consequently, on the nursing infant. The primary active ingredients in whitening products, such as hydrogen peroxide and carbamide peroxide, can potentially be absorbed into the bloodstream. Though the amount absorbed might be small, there’s a theoretical risk of these chemicals transferring into breast milk. This is because a nursing infant’s developing system is more vulnerable to the potential effects of any substances in breast milk. Many dental professionals recommend avoiding tooth whitening while breastfeeding due to the lack of conclusive safety data. Consulting with a dentist and your pediatrician is crucial to making an informed decision based on your individual circumstances.
Potential Risks of Tooth Whitening
Tooth whitening, while generally safe for most adults, carries certain risks. The most common side effect is tooth sensitivity, which can range from mild to moderate and usually subsides shortly after treatment. Gum irritation or inflammation is another potential issue, especially if the bleaching agent comes into contact with the gums. In rare cases, tooth whitening can cause changes in the tooth enamel, making them more susceptible to damage. The effectiveness of tooth whitening varies depending on the type and severity of the stains, as well as the individual’s tooth structure. For pregnant or breastfeeding women, the risks are heightened because of the potential for chemical absorption and transfer to the baby. Always consult with a dentist to assess your oral health. They can guide you on the suitability of tooth whitening and minimize potential risks.
Chemical Absorption and Milk Transfer
The primary concern with tooth whitening during breastfeeding revolves around the potential for chemical absorption into the bloodstream and subsequent transfer into breast milk. The active ingredients in whitening products, typically hydrogen peroxide and carbamide peroxide, can be absorbed through the tooth enamel and the oral tissues. While the amount absorbed may be small, the transfer to breast milk is a concern. These chemicals could then be ingested by the nursing infant. The infant’s developing body is more sensitive to the effects of any substances in breast milk. Though there’s limited research on the exact effects of these chemicals on infants. Dental and medical professionals often err on the side of caution, advising against tooth whitening during breastfeeding to minimize any potential risks to the baby. The lack of definitive safety data underscores the importance of informed decision-making and professional guidance.
Effects on the Baby’s Health
The potential effects of tooth whitening agents on a baby’s health are a key consideration for breastfeeding mothers. While the precise impact is not fully understood due to limited research, the primary concern is the baby’s exposure to chemicals, potentially through breast milk. The infant’s developing systems are more vulnerable to the effects of any substances ingested. The long-term consequences of exposure to these whitening agents are currently unknown. Therefore, many healthcare providers recommend avoiding tooth whitening while breastfeeding to minimize any potential risks. If a mother chooses to proceed with tooth whitening, the potential effects on the baby’s health must be carefully considered. This decision should be made in consultation with both a dentist and a pediatrician, weighing the benefits of tooth whitening against the potential risks to the infant.
Top 5 Facts About Tooth Whitening and Breastfeeding
Fact 1 The Ingredients
The primary active ingredients in tooth whitening products are hydrogen peroxide and carbamide peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide is a strong oxidizing agent used in higher concentrations for professional whitening, whereas carbamide peroxide breaks down into hydrogen peroxide and urea. These chemicals penetrate the tooth enamel to break down stains. The concentration of these ingredients varies depending on the product type – in-office treatments often use higher concentrations. At-home kits contain lower concentrations. Both substances can be absorbed into the bloodstream and potentially transferred to breast milk. This highlights the importance of understanding the ingredients and their potential impact during breastfeeding.
Fact 2 Consultation Is Key
Before considering tooth whitening while breastfeeding, a consultation with both your dentist and your pediatrician is essential. Your dentist will assess your oral health, discuss the different whitening options, and explain the potential risks and benefits. They can provide personalized advice. Your pediatrician can provide guidance on the potential effects on your baby, considering the limited research available. During this consultation, you can discuss your concerns. You can weigh the decision based on your specific circumstances. Open communication with healthcare professionals ensures you make an informed choice that prioritizes the health of both you and your baby. They can help you understand the potential risks versus the desire for whiter teeth.
Fact 3 Professional Guidance

Always seek professional guidance from a dentist before undergoing any tooth whitening procedure, especially during breastfeeding. A dentist can evaluate your oral health, identify any pre-existing conditions, and recommend the most suitable whitening method. They can also monitor the progress and address any potential side effects, such as tooth sensitivity or gum irritation. Professional guidance ensures the procedure is safe and effective. It helps minimize any potential risks. The dentist can tailor the treatment to your specific needs and provide recommendations on how to maintain your results. Following professional advice is essential to protect your oral health and make informed decisions about your dental care during breastfeeding.
Fact 4 Consider Timing
If you’re considering tooth whitening while breastfeeding, carefully consider the timing. Many dental professionals advise postponing the procedure until after you have weaned your baby. This approach minimizes the risk of any potential harm to the infant. If you’re unable to postpone tooth whitening, have an open discussion with your dentist and pediatrician. Discuss the potential risks and benefits. Assess the baby’s age and overall health. Factors like the frequency and duration of breastfeeding also play a role. Some mothers choose to wait until they are exclusively formula-feeding their babies. Then they can pursue tooth whitening. This choice should be based on your specific circumstances and the guidance of healthcare professionals.
Fact 5 Prioritize Baby’s Health
The health and well-being of your baby should always be the top priority when making any decisions about your health and dental care. During breastfeeding, any substances you consume or are exposed to can potentially affect your baby through breast milk. The limited research on the safety of tooth whitening during breastfeeding emphasizes the importance of caution. Making informed decisions that prioritize the health of your baby is critical. This includes consulting with your dentist and pediatrician. Weighing the benefits of tooth whitening against the potential risks to your infant. It might involve considering alternative options, such as waiting to whiten your teeth until after weaning. Ensuring your baby’s health remains the guiding principle when considering teeth whitening while breastfeeding.
Alternative Teeth Whitening Methods for Breastfeeding Moms
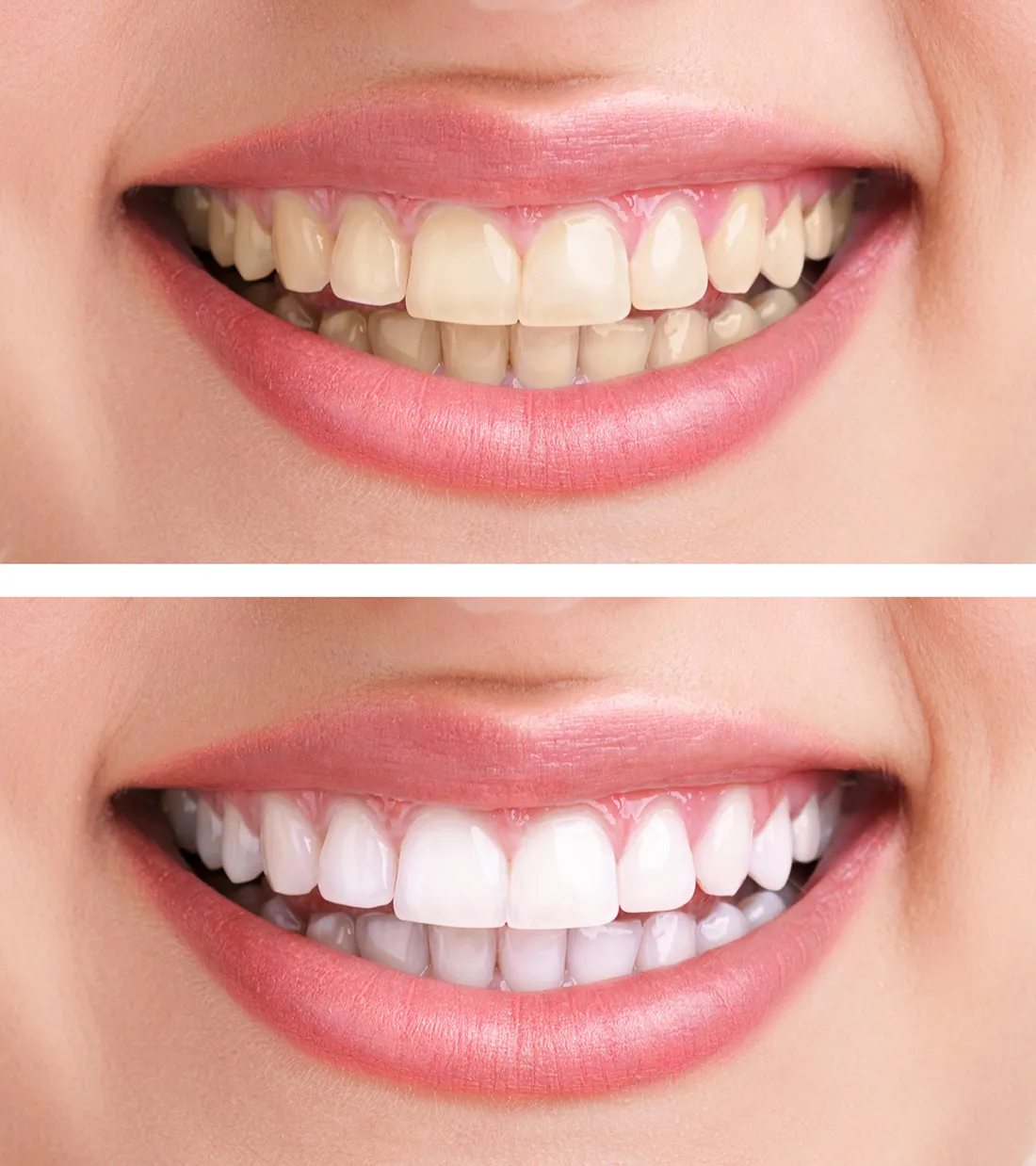
While tooth whitening with bleaching agents may be a concern during breastfeeding, there are alternative options to improve the appearance of your teeth. These methods offer safer ways to brighten your smile while prioritizing your baby’s health. You can achieve noticeable improvements in the brightness of your teeth without exposing your baby to any potential risks associated with bleaching agents. These alternatives help to maintain a radiant smile without compromising the safety of breastfeeding.
Natural Remedies
There are natural remedies that may help to whiten teeth gently. These include brushing with baking soda, which has mild abrasive properties that can help remove surface stains. However, use it sparingly as excessive use can erode enamel. Oil pulling with coconut oil is another alternative. It involves swishing the oil in your mouth for about 15-20 minutes. It is believed to remove bacteria and toxins. Another option is brushing with a mixture of turmeric and coconut oil. Turmeric has natural whitening properties. But the effectiveness of these methods varies. They’re generally milder and less likely to cause side effects. Consult with your dentist before using natural remedies. It makes sure they are appropriate for your oral health. Also, if you are unsure about the natural remedies, always follow your doctor’s or dentist’s recommendations.
Good Oral Hygiene Practices
Maintaining excellent oral hygiene is essential for keeping your teeth bright and healthy, even during breastfeeding. This involves brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste. Flossing daily to remove plaque and food particles between teeth is also important. Rinsing your mouth with water after meals can help remove food debris and prevent stains. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are also vital for removing plaque and tartar buildup, which can cause discoloration. Avoiding sugary drinks, snacks, and tobacco products is also important. This helps minimize stains and protect your teeth. Proper oral hygiene practices not only maintain the brightness of your smile but also protect your overall oral health. It is always important to follow the dental professional’s recommendations.
