What are White Spots on Teeth?
White spots on teeth, often appearing after using teeth whitening trays, can be a cosmetic concern for many. These spots, which can vary in size and prominence, are areas where the enamel has become less mineralized. This change in the enamel’s structure alters how light reflects off the tooth’s surface, resulting in a white or opaque appearance. They are most noticeable when the rest of the tooth’s surface becomes whiter due to the whitening process, making the spots stand out even more. Understanding the underlying causes of these spots is crucial for both prevention and treatment. Addressing these white spots involves understanding the causes behind the changes in tooth enamel and exploring effective treatment options that can restore a uniform appearance and enhance the overall aesthetic of your smile. It is important to consult with a dental professional for a proper diagnosis and personalized advice tailored to your specific situation.
Causes of White Spots After Whitening Trays
Several factors contribute to the formation of white spots on teeth, particularly after the use of teeth whitening trays. These factors often relate to changes in the enamel’s mineral content or the way the whitening agents interact with the tooth surface. Identifying these causes is essential for understanding the phenomenon and implementing preventive measures. The most common causes include demineralization of the enamel, uneven whitening, and, in some cases, the presence of fluorosis. Each of these factors can lead to the appearance of white spots, influencing the overall aesthetics of the teeth and requiring specific approaches for management. Proper tray usage, the choice of whitening agent, and maintaining good oral hygiene play critical roles in minimizing the risk of white spots. Understanding the interplay between these causes helps in developing effective strategies to preserve the uniformity and health of your teeth during and after the whitening process.
Demineralization
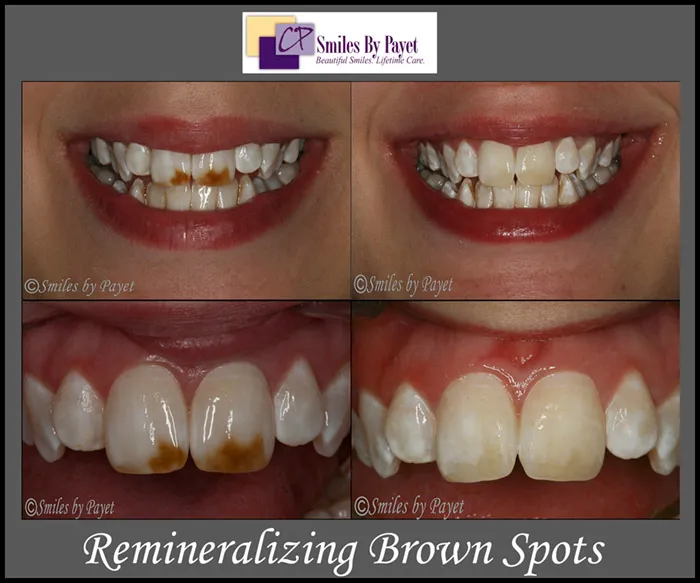
Demineralization is a primary cause of white spots on teeth. It happens when acids, often produced by bacteria in the mouth, erode the enamel, leading to a loss of minerals like calcium and phosphate. This process creates porous areas on the tooth surface, which appear white because they reflect light differently than the surrounding, more mineralized enamel. Whitening trays, if used improperly or with high concentrations of bleaching agents, can exacerbate demineralization. The extended contact with the whitening agent can temporarily weaken the enamel, making it more susceptible to mineral loss. Dietary habits, such as frequent consumption of sugary or acidic foods, can worsen demineralization, heightening the risk of white spot formation. Proper oral hygiene practices, including consistent brushing and flossing, are essential to counteract the demineralization process and preserve enamel integrity. Furthermore, using a fluoride toothpaste can help remineralize the enamel, strengthening it and reducing the appearance of white spots.
Uneven Whitening
Uneven whitening is another key contributor to the appearance of white spots. The whitening process isn’t always uniform across the entire tooth surface. Areas with thinner enamel or those naturally less mineralized may absorb the whitening agent more rapidly, leading to a faster whitening effect compared to the rest of the tooth. Existing dental conditions, like enamel hypoplasia, where the enamel is underdeveloped, can result in uneven whitening and accentuate white spots. The concentration of the whitening agent, the duration of its application, and the individual tooth’s characteristics all play a role. Some teeth might have naturally occurring variations in their mineral density. For instance, the edges of teeth can sometimes show more whitening due to the enamel’s structure. Addressing uneven whitening requires careful application techniques. This could include the use of customized whitening trays. These trays ensure even distribution of the agent and can help prevent or minimize the contrast between the whitened and unwhitened areas. Consulting with a dentist is helpful to develop a tailored whitening plan.
Fluorosis
Fluorosis is a dental condition that arises from excessive fluoride exposure during tooth development. It can manifest as white spots, streaks, or even brown discoloration on the enamel. Fluoride, while beneficial for strengthening teeth, can disrupt the enamel formation process when taken in excess during childhood, before teeth have fully developed. The severity of fluorosis varies depending on the amount of fluoride ingested and the stage of tooth development. Mild cases might present as barely noticeable white spots, whereas severe cases can lead to significant staining and pitting of the enamel. Fluorosis is not typically caused by teeth whitening trays themselves, but the whitening process can make the existing white spots more noticeable by bleaching the surrounding enamel. The presence of fluorosis underscores the importance of monitoring fluoride intake, especially in children. Prevention includes controlling the amount of toothpaste used, avoiding fluoride supplements unless recommended by a dentist, and ensuring children do not swallow toothpaste while brushing. Treatment options range from cosmetic procedures like microabrasion to more invasive interventions like veneers or crowns, depending on the severity and aesthetic impact of the condition.
How to Prevent White Spots with Whitening Trays
Preventing white spots when using teeth whitening trays involves several key strategies. These strategies focus on proper application, the choice of whitening agents, and maintaining optimal oral hygiene. By understanding and implementing these practices, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of white spots while still achieving a brighter smile. Consistency and attention to detail are essential for success. Regular dental check-ups are also important. They help in the early detection of any issues. Following the guidelines will help to ensure that your teeth whitening experience is both effective and safe. This will help you to achieve the desired results without compromising the health and appearance of your teeth.
Proper Tray Usage
Proper tray usage is fundamental in preventing white spots during teeth whitening. Ill-fitting trays can lead to uneven distribution of the whitening agent, resulting in localized overexposure and potential demineralization. It is critical to ensure the trays fit snugly over your teeth. Make sure they cover all tooth surfaces evenly. Follow the instructions provided by your dentist or the manufacturer. This will ensure that the agent is applied correctly. Avoid overfilling the trays. Excess gel can leak and cause irritation to the gums and soft tissues, which can further impact the whitening process. Adhering to the recommended treatment duration and frequency is also crucial. Prolonged or excessive use can increase the risk of enamel damage. Regularly clean and maintain the trays. This prevents the buildup of bacteria and the contamination of the whitening agent. Consulting a dental professional for customized trays and guidance on their proper use is always a good idea. It ensures the most effective and safest teeth whitening experience.
Using the Right Whitening Agent
Choosing the right whitening agent plays a critical role in minimizing the risk of white spots. The concentration of the active ingredient, typically hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, is a key factor. Higher concentrations can lead to faster whitening. They also increase the risk of enamel sensitivity and white spot formation. Consulting with a dentist can help determine the appropriate concentration for your specific needs and enamel sensitivity. Following the dentist’s recommendations helps reduce the chances of adverse effects. The type of whitening agent can also influence the outcome. Some formulations include ingredients designed to protect enamel or enhance remineralization. These can help to buffer against potential damage. Look for products that contain fluoride. This aids in strengthening the enamel and reducing sensitivity. Always follow the instructions on the product label. Do not exceed the recommended dosage or duration. Be aware of the potential side effects. If you experience any discomfort, discontinue use and seek professional advice.
Maintaining Oral Hygiene
Maintaining impeccable oral hygiene is crucial not only for overall dental health but also for preventing white spots during teeth whitening. Consistent and proper brushing with a fluoride toothpaste helps in removing plaque and preventing demineralization. Flossing daily removes food particles and plaque from between the teeth, areas that are often more susceptible to white spot formation. Rinsing with an antibacterial mouthwash can further reduce bacteria, which produce acids that erode enamel. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are essential. They remove any stubborn plaque or tartar build-up that can contribute to enamel damage. Make sure to limit the consumption of sugary and acidic foods and beverages. These can erode the enamel and increase the risk of white spots. Drinking plenty of water helps to rinse away food particles and neutralize acids in the mouth. Following these practices will help ensure your teeth remain healthy and beautiful, and minimizing the risk of white spots during whitening.
Treatments for White Spots on Teeth
Fortunately, several effective treatments are available for addressing white spots on teeth. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the spots and the individual’s aesthetic goals. Consulting with a dentist is the first step. They can assess the extent of the white spots and recommend the most appropriate course of action. Treatment options vary from minimally invasive procedures, aimed at improving the appearance of the enamel, to more comprehensive interventions designed to restore the natural look and feel of your teeth. Each treatment has its advantages and considerations. Your dentist can help you understand the pros and cons of each option. This way, you can make an informed decision. This will lead to the most satisfying and effective solution for achieving a brighter, more uniform smile.
Microabrasion
Microabrasion is a conservative treatment option for removing superficial white spots. This procedure involves gently polishing the enamel’s surface with a mixture of abrasive materials and acid. The process removes a thin layer of enamel, effectively blending the white spots with the surrounding tooth structure. It is most suitable for mild to moderate white spots that are primarily surface-level. Microabrasion is generally a quick and painless procedure, often completed in a single dental visit. It can significantly improve the appearance of the teeth. Following microabrasion, the teeth may be further polished and treated with fluoride to strengthen the enamel. The results of microabrasion can be long-lasting, particularly when combined with proper oral hygiene practices. This is a cost-effective solution and is a great starting point for addressing white spots before considering more extensive treatments. If the white spots are deeper or more extensive, microabrasion may not be sufficient. Other treatments, such as resin infiltration, may be more appropriate.
Teeth Whitening
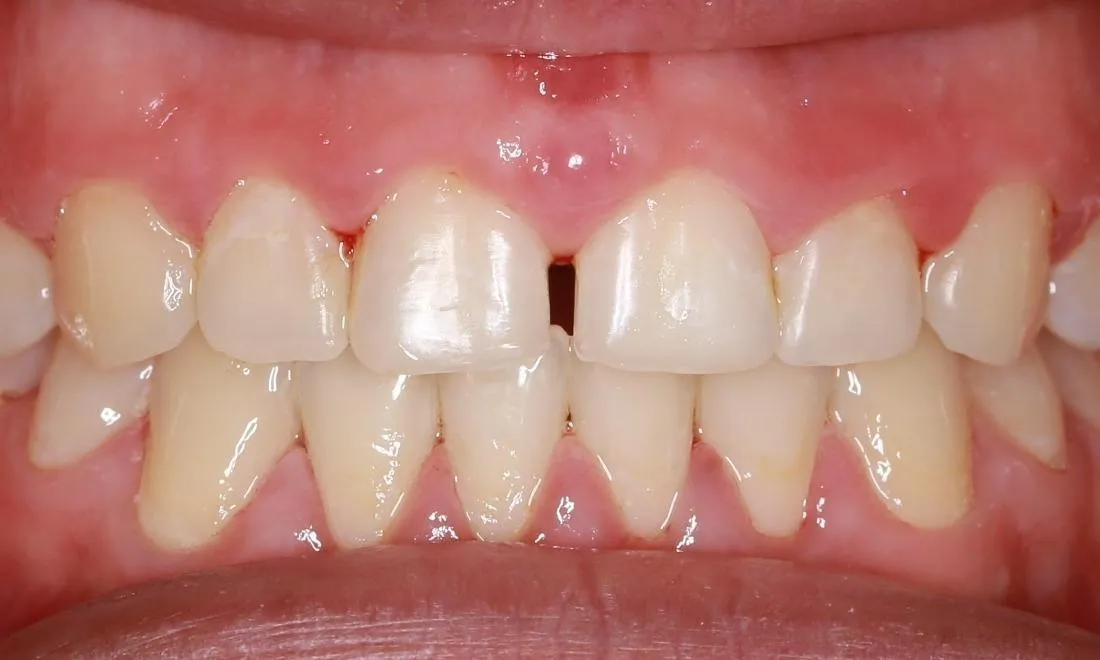
Teeth whitening can sometimes help to minimize the contrast between white spots and the surrounding enamel. By whitening the overall tooth surface, the spots may appear less noticeable. This approach is particularly useful when the white spots are less pronounced or when the goal is to improve the overall brightness of the smile. Professional teeth whitening procedures, performed by a dentist, often use stronger bleaching agents than over-the-counter products. This leads to more effective and longer-lasting results. During the whitening process, the dentist can monitor the teeth. They ensure even results and minimize the risk of further enamel damage. In some cases, teeth whitening can be combined with other treatments, such as microabrasion or resin infiltration. This approach can maximize aesthetic outcomes. While teeth whitening can improve the appearance, it is essential to recognize that it does not eliminate the white spots. The effect depends on the severity and the nature of the white spots.
Resin Infiltration
Resin infiltration is an innovative treatment that addresses white spots by filling the porous areas of the enamel with a resin material. The process involves the application of an acid to open up the enamel’s pores. Then, a special resin is applied. It penetrates the enamel and fills in the demineralized areas. This effectively masks the white spots and improves the overall appearance of the tooth. Resin infiltration is particularly effective for treating white spots caused by demineralization. The resin has a similar refractive index to the enamel, which minimizes the contrast and creates a more natural look. This is a minimally invasive procedure that requires minimal or no drilling. It offers a significant aesthetic improvement without the need for more aggressive treatments. Resin infiltration is often a good option for those who are not candidates for microabrasion. The results can be long-lasting, provided good oral hygiene is maintained. Regular dental check-ups help to monitor the treated areas. They also ensure the long-term success of the treatment.
Professional Dental Cleanings
Regular professional dental cleanings are essential for maintaining overall oral health and preventing the worsening of white spots. During a cleaning, the dental hygienist removes plaque and tartar buildup. They also polish the teeth. These actions contribute to reducing the appearance of white spots. Professional cleaning also helps remove surface stains. This helps brighten the teeth and improves their overall appearance. The dental hygienist can also identify early signs of demineralization or enamel erosion. Early detection allows for timely intervention to prevent the formation of white spots. Professional cleanings often include fluoride treatments. Fluoride strengthens the enamel and can help in the remineralization of areas affected by white spots. Regular dental check-ups also allow the dentist to monitor the health of the teeth. They can identify any underlying issues that may contribute to white spots. Scheduling these visits every six months is a proactive step. This helps to preserve the health and aesthetics of your smile. Professional cleanings are a key part of a comprehensive oral hygiene routine. They help prevent and manage white spots effectively.
